.jpg)

 Product Name: Vanadium Carbide (VC)
Product Name: Vanadium Carbide (VC)
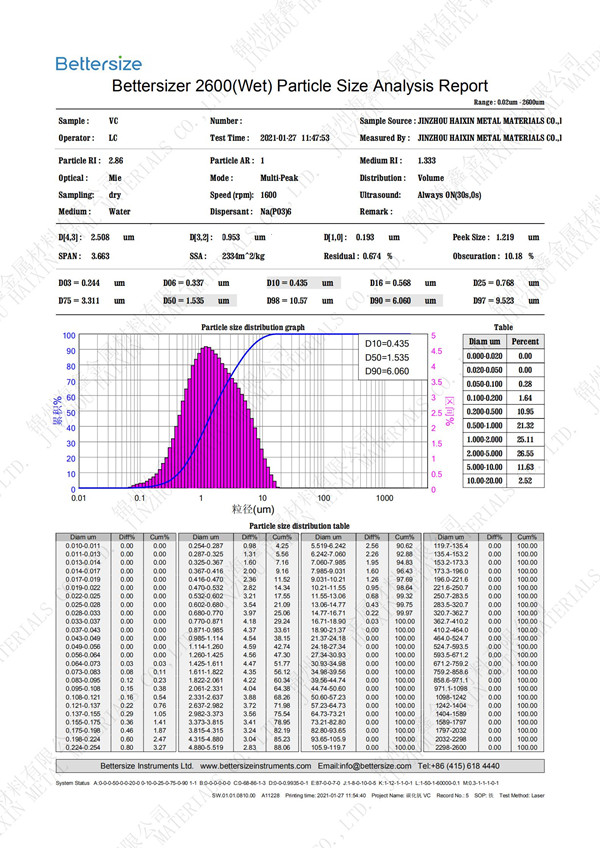
Specification: 0.8-10um (D50)
Appearance: Irregular
Color: Black Grey
Features: high hardness, high melting point and high temperature strength, good conductivity and thermal conductivity
Application: In the fields of steel metallurgy, hard alloys, electronic products, catalysts, and high-temperature coating materials, etc







.jpg)
Vanadium carbide
Molecular formula: VC
Cas:12070-10-9
Appearance: Grey black powder
Melting point: 2800 ° C
Density: 5.41g/cm3
Molecular weight: sixty-two point nine five
Performance characteristics of vanadium carbide:
1. High melting point: Vanadium carbide has a melting point of around 2810 ° C, making it one of the compounds with the highest melting point so far. Therefore, vanadium carbide has good stability in high temperature environments.
2. Corrosion resistance: Vanadium carbide has good corrosion resistance and can play a good role in corrosive environments such as acid, alkali, and salt.
3. High hardness: Vanadium carbide has extremely high hardness, reaching 9.0 or above in Mohs hardness testing, which is much higher than the hardness of common metals such as steel and aluminum.
4. High wear resistance: Vanadium carbide has excellent wear resistance and can play an important role in high-speed cutting, radar transmission, and other applications.
Product application:
1. Hard alloy and cutting tools
Vanadium carbide is often used as an additive in hard alloys, combined with tungsten carbide (WC), titanium carbide (TiC), etc., for the manufacture of cutting tools, drill bits, and molds. Advantages: Its high hardness and wear resistance can significantly improve the service life and processing efficiency of tools, especially in high-speed cutting and precision machining.
2. Surface engineering and wear-resistant coatings
By using physical vapor deposition (PVD) or chemical vapor deposition (CVD) techniques, vanadium carbide coatings are applied to the surfaces of cutting tools, molds, or mechanical components. Advantages: Enhanced surface hardness (up to 2800-3200 HV) and wear resistance, suitable for high temperature or corrosive environments.
3. High temperature structural materials
In the aerospace and nuclear industries, vanadium carbide is used to manufacture components that require extreme high temperatures, such as turbine blades and combustion chamber parts. Advantages: High melting point (about 2830 ° C) and good thermal stability, suitable for long-term high-temperature operation.
4. Catalysts and catalytic carriers
In the field of chemical engineering, vanadium carbide is used as a catalyst to participate in dehydrogenation, hydrogenation and other reactions, especially in petroleum refining and ammonia synthesis processes. Advantages: High specific surface area and chemical inertness, improving reaction efficiency and selectivity.
5. Composite material reinforcement phase
Application: As reinforcing particles added to metal (such as aluminum, titanium) or ceramic matrices to improve the mechanical properties of composite materials. Advantages: Significantly improve the strength, toughness, and wear resistance of materials, suitable for automotive and aerospace structural components.
6. Electronics and Conductive Materials
Used for preparing conductive coatings in high-temperature electrodes or electronic devices. Advantages: Good conductivity and oxidation resistance, suitable for high-frequency electronic devices and sensors.
7. Nuclear industry applications
As a neutron reflector or structural material, used for nuclear reactor components. Advantages: Low neutron absorption cross-section and radiation resistance, enhancing reactor safety and lifespan.
8. Refractory materials
As a refractory material in high-temperature furnace lining or smelting equipment. Advantages: Excellent high-temperature stability and thermal shock resistance, extending the service life of equipment.
9. Energy storage and battery materials
Study its application in lithium-ion batteries or supercapacitors as electrode materials. Advantages: High theoretical capacity and fast charging and discharging performance, with potential in the next generation of energy storage systems.
10. Anti corrosion coating
Used in chemical equipment or marine environments to protect metal components from corrosion. Advantages: Resistant to acid, alkali, corrosion, and oxidation, suitable for harsh chemical environments.
Packaging and storage: This product is packaged in an inert gas filled plastic bag, sealed and stored in a dry and cool environment. It should not be exposed to air to prevent moisture from causing oxidation and aggregation, which may affect dispersion performance and usage effectiveness; The packaging quantity can be provided according to customer requirements and divided into smaller packages.

Technological innovation
Honesty is the foundation
Contact Number: +86-15698999555 |
Address: NO.6 ,SHENGHUA STREET,TAIHE DISTRICT, JINZHOU CITY, LIAONING PROVINCE, CHINA. |