On August 19th, Cailian News Agency announced that the South Korean
Institute of Science and Technology (KIST) announced on Thursday
(August 17th) that it had developed a new technology for mass production
of "MXene", which is expected to open the path to mass production that
is still not achievable so far.
It is reported that MXene is a type of two-dimensional inorganic
compound in materials science. These materials are composed of
transition metal carbides, nitrides, or carbonitrides with several
atomic layer thicknesses. It was first discovered in 2011, due to
the presence of hydroxyl groups or terminal oxygen on the surface of
MXene materials, which have the metal conductivity of transition
metal carbides.
Due to its unique performance, MXene has quickly become a research
hotspot and one of the most concerned two-dimensional nanomaterials after
graphene. It has been widely used in many fields such as energy storage,
catalysis, adsorption, and so on.
However, the large-scale preparation of MXene is still relatively
difficult, and related research is still in its infancy. More than 30
different types of MXene materials have been discovered, which can be
adjusted and optimized according to different application requirements.
KIST published this paper in the journal Nanoscale, and the researchers
stated that MXene has different application fields depending on the Hall
scattering factor. When the value is less than 1, it can be used for
high-performance transistors, high-frequency generators, high-efficiency
sensors, photodetectors, etc. If the value is greater than 1, it can be
used for thermoelectric materials and magnetic sensors, etc.
Lee Seung chul, Director of the KIST South Korea India Cooperation
Center, wrote in a statement: "Unlike previous studies that focused on
the production and characteristics of pure MXene, we have developed a
new surface molecular analysis method that can easily classify manufactured
MXene materials, which is a crucial step. Based on this, we anticipate that
mass production of MXene materials with uniform quality will become possible
What is MXene?

MXene is a two-dimensional inorganic compound composed of transition
metal carbides, nitrides, or carbonitrides, with a thickness of only a
few atomic layers, resulting in extremely high specific surface area and
conductivity. The name MXene comes from its structure similar to MAX
phase materials (M is a transition metal, A is the main group element,
and X is carbon or nitrogen), but element A is etched out, forming a
layered structure of Mn+1Xn (n=1,2,3). Due to the presence of functional
groups such as hydroxyl or terminal oxygen on the surface of MXene, it
has hydrophilicity and adjustable surface chemistry.
Since its first discovery in 2011, MXene has attracted widespread
attention from both the scientific and industrial communities, and is
considered one of the most promising two-dimensional nanomaterials after
graphene. Due to its excellent electrical, optical, thermal, mechanical,
and catalytic properties, MXene has shown enormous potential in various
fields such as energy storage, sensors, electronic devices, biomedical,
and environmental engineering.
The Application of MXene in the Field of Life Sciences
Biosensor: MXene can serve as a high-performance receptor for detecting
the state and function of biomolecules, cells, tissues, and organs. MXene
can be combined with different types of sensors such as fluorescence, optics,
electrochemistry, and field-effect transistors to achieve high selectivity,
low detection limit, high sensitivity, and fast response in biological detection.
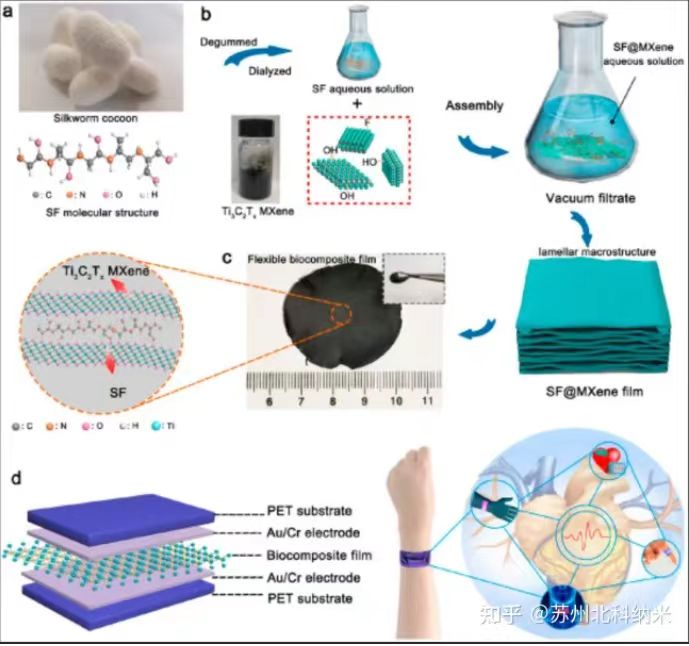
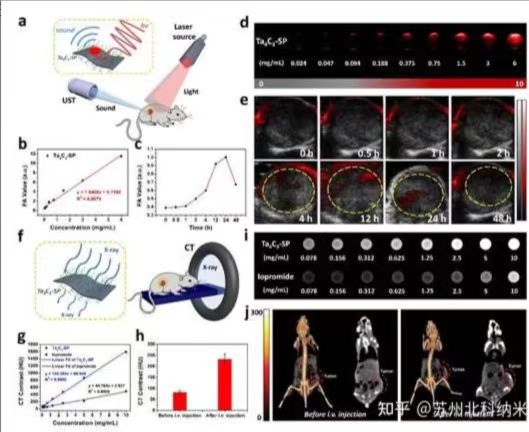
Bioimaging: MXene can be used as a multifunctional imaging agent to
improve the diagnostic efficiency and accuracy of tumors and other diseases.
MXene can utilize its strong absorption ability in the near-infrared region
and high attenuation performance of X-rays to enhance various imaging modes
such as photoacoustic imaging, photothermal imaging, and X-ray computed tomography.
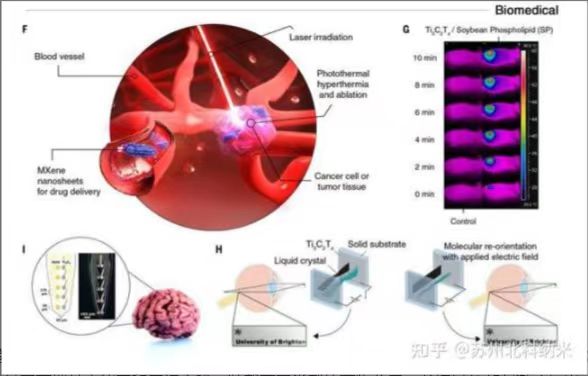
Drug delivery: MXene can serve as an effective drug carrier for
targeted drug delivery and controlled release. MXene can load different
types of drug molecules through its surface terminal functional groups
and interlayer gaps, and trigger drug release through external stimuli
such as light, heat, electricity, or enzymes.
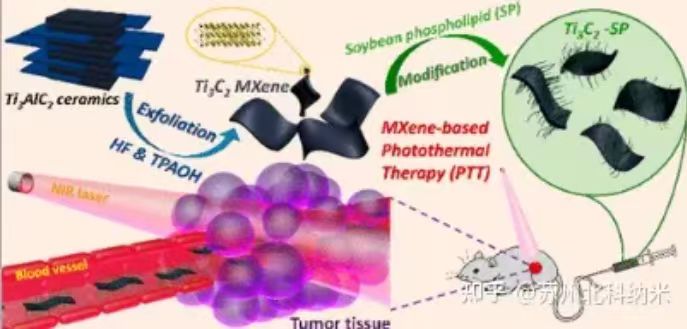
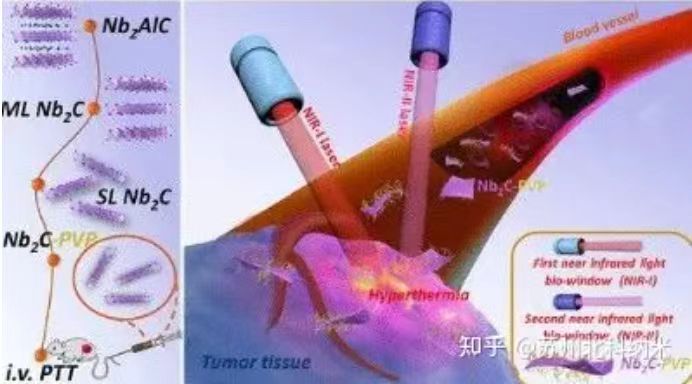
Photothermal therapy: MXene can be used as an efficient photothermal
agent to achieve thermal ablation of tumors and other pathological tissues.
MXene can convert absorbed light energy into heat energy through its high
photothermal conversion efficiency in the near-infrared region, and increase
the local temperature to a level sufficient to kill cancer cells.
Implants: MXene can be used as a material with good biocompatibility
and electrical properties to prepare implantable medical devices, such as
artificial bones, cardiac pacemakers, nerve stimulators, etc. MXene can
form a good interface with human tissues and achieve signal transmission
and regulation through its excellent mechanical toughness and conductivity.
summary
If this study breaks through the key technical challenges of large-scale
preparation of MXene and develops a simple method to distinguish different
MXene materials. So this not only reduces the manufacturing cost of MXene,
but also lays the foundation for achieving its commercial application. Based
on the specific type and performance indicators of MXene, customized production
of MXene for specific purposes can be achieved.
This provides a guarantee for the widespread application of MXene in
biomedical, high-performance electronic devices, sensors, thermoelectric conversion,
energy storage, and other fields. The implementation of large-scale production of
MXene will greatly promote the transformation of MXene scientific research achievements
into practical applications, solve practical problems in the process of industrial
development, and its scientific research achievements have significant scientific
significance and broad application prospects.
Technological innovation
Honesty is the foundation
Contact Number: +86-15698999555 |
Address: NO.6 ,SHENGHUA STREET,TAIHE DISTRICT, JINZHOU CITY, LIAONING PROVINCE, CHINA. |